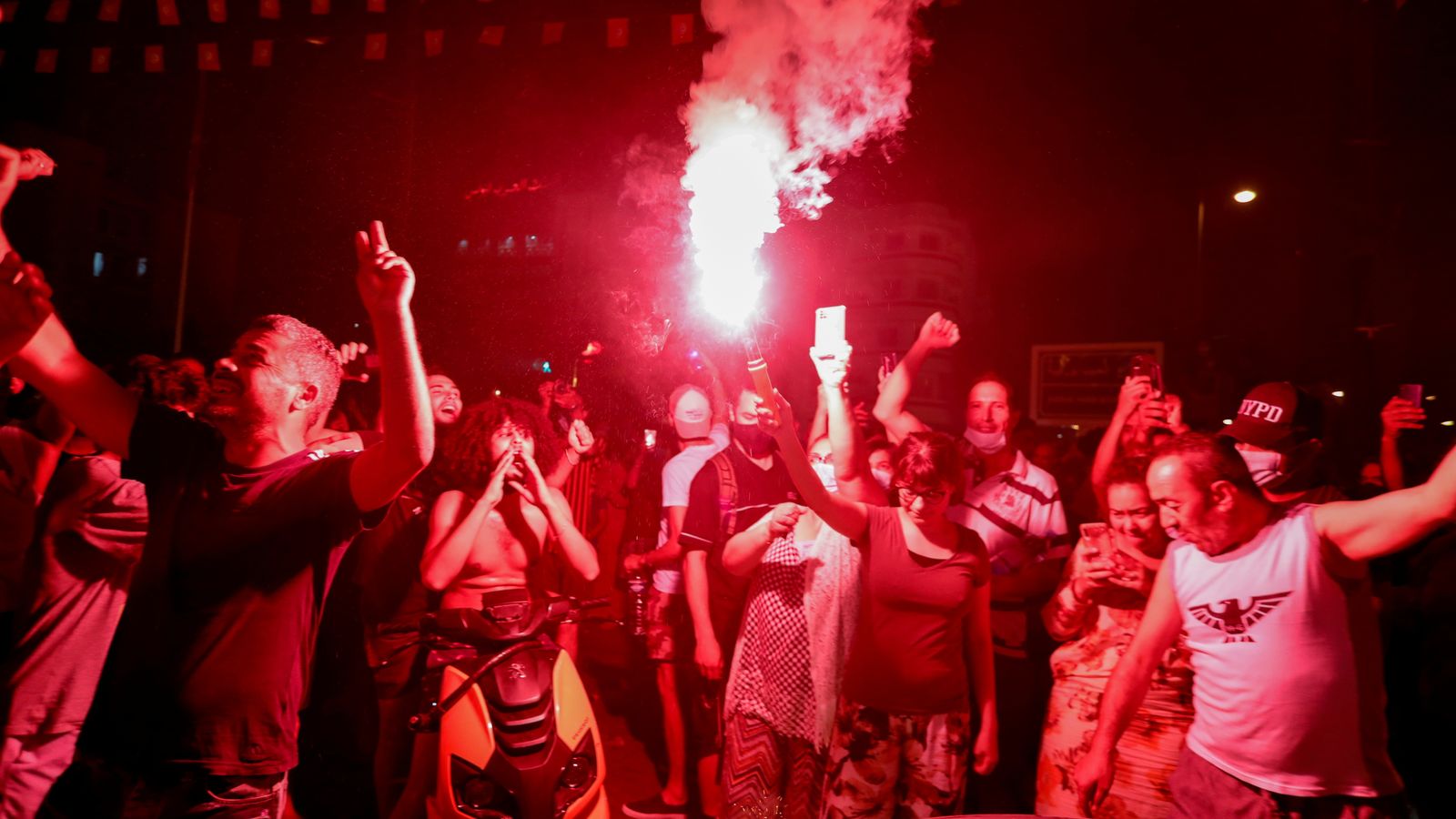
Long considered one of the few success stories that sprang from the Arab Spring, Tunisia has seen its president accused of staging a coup after he sacked his prime minister and suspended parliament with the help of the army.
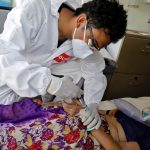
President Kais Saied’s dismissal of Prime Minister Hichem Mechichi on Sunday followed violent demonstrations across the country over the government’s handling of the coronavirus pandemic.
It has led to clashes between supporters and opponents of the president in the streets of the capital, Tunis.
Mr Saied has said he will name a new prime minister, but his critics have accused him of a power grab that threatens Tunisia‘s young democracy.
Here is a look at the legacy of the Arab Spring and how protests and uprisings dramatically altered the political structure of much of the Arab world.
The Arab Spring
The Arab Spring spread across much of the Arab world from early 2010 as demonstrators rallied against the region’s dictatorial leaders in protests over corruption, poverty and oppression.
Escalating anti-government protests spilt over into uprisings and eventually civil wars in several countries as the Arab Spring spread from Tunisia to Egypt, Syria, Libya and Yemen, resulting in the ousting of the leaders in those countries, with the exception of Syria.
It has directly contributed to the refugee crisis and the rise of the Islamic State and has seen fresh authoritarian leaders seize power in many countries, leaving many with their hopes crushed as they struggle to live under increasingly authoritarian regimes in countries beset by greater levels of poverty and unemployment.
Tunisia
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
The roots of the Arab Spring can be traced back to Tunisia, where Mohamed Bouazizi, a fruit seller, set himself on fire in protest after police confiscated his goods and a female officer slapped him on 17 December 2010.
Footage of his self-immolation spread across the country and led people in his home city of Sidi Bouzid to take to the streets in rage.
Within a month, protests had forced Tunisia’s authoritarian president, Zine El Abidine Ben Ali, to flee to Saudi Arabia.
Despite the relative success of Tunisia’s revolution, the country has recently seen large protests over mass unemployment and many consider its parliament inefficient and stagnant.
These problems have been exacerbated by the coronavirus pandemic, which has hit the economy hard as infection rates soared over the summer.
Egypt
Demonstrations in Tunisia following the death of Bouazizi inspired massive protests across Egypt, leading President Hosni Mubarak to leave office within weeks.
A presidential election in 2012 gave power to President Mohammed Morsi and the Muslim Brotherhood, but Mr Morsi himself was later deposed when Egypt’s military generals seized power in 2013.
Field Marshal Abdul Fattah al-Sisi then became president and imposed a police state, which has seen tens of thousands of Egyptians imprisoned and hundreds executed.
The country remains under military rule.
Syria
As unrest spread across Syria, Bashar al Assad’s government began using live ammunition against protesters, leading tensions to boil over and igniting a civil war in 2011 between the regime and rebel groups.
IS emerged from among the myriad rebel groups and expanded across the border into Iraq, where it declared a new Islamic caliphate in 2014.
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
Syria’s brutal decade-long civil war has seen hundreds of thousands of people killed and over 6.8 million Syrians become asylum seekers and 6.7 million displaced within the country’s borders.
Despite this, Mr Assad has managed to cling on to power with the support of Russia, Iran and Lebanon-based Shia-militant group Hezbollah, although fighting in the war-ravaged country continues and several areas remain under the control of rebels.
Libya
Similarly, Libya’s Muammar Gaddafi decided to crack down on the largest protests in the country’s history with force.
The move sparked a civil war and a NATO-led coalition began conducting airstrikes in support of the country’s rebels.
Rebel forces deposed and later killed Gaddafi in October 2011. However, efforts to transition away from Gaddafi’s rule broke down and the country descended into a renewed civil war.
The internationally recognised Government of National Accord remains in control of Tripoli and the city of Misrata, while the Libyan National Army, commanded by General Khalifa Haftar, runs Benghazi and much of the oil-rich east. General Haftar’s forces are supported by Russia, Egypt and the United Arab Emirates.
Yemen
As protests spread throughout much of the Arab world, pressure on Yemen’s authoritarian president Ali Abdullah Saleh led him to hand power to his deputy, Abdrabbuh Mansour Hadi, in 2011.
However, Mr Hadi’s presidency was beset by continuing problems of corruption, unemployment and an insurgency from the Houthi militia.
The Houthis took control of the capital, Sana’a, in 2014 and declared themselves in charge of the government. Yemen’s President, Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, fled to Aden, where he continues to lead Yemen’s internationally-recognised government.
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
Fierce fighting between the Iran-backed Houthi group and the western-backed coalition led by Saudi Arabia has led to one of the worst famines the world has ever seen, with half of the population lacking food and almost 16 million on the brink of starvation in 2016.
Other countries affected
While the Arab Spring saw rulers deposed in Tunisia, Libya, Egypt and Yemen, it also led to street protests in Iraq, Morocco, Algeria, Lebanon, Jordan, Kuwait, Oman and Sudan. Some countries, such as Saudi Arabia, were able to use military force to effectively end revolts before they could seriously threaten the status quo.
Legacy of the Arab Spring
While the reverberations of the Arab Spring continue to affect life in the Arab World, continuing issues including corruption, authoritarianism and poverty are likely to be exacerbated by the coronavirus crisis.
Only Tunisia’s uprising resulted in a transition to a constitutional democracy, but with the country’s president ousting his prime minister, the shift away from authoritarian rule is looking increasingly fragile.