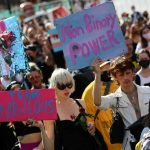The sister of a teenager shot dead on Bloody Sunday, 50 years ago this weekend, has urged the soldier who fired the fatal shot to admit it.
Kay Duddy, 75, says her brother Jackie, 17, cannot rest until that happens and is directly appealing to former members of the British Parachute Regiment.
She said: “Please put your hands up and say you did it, so we can lay our wee brother to rest.
“My wee brother, Jackie Duddy, has been buried for 50 years but up to this minute in time, he hasn’t been laid to rest.
“How can you lay somebody to rest without justice for what happened that awful day?”
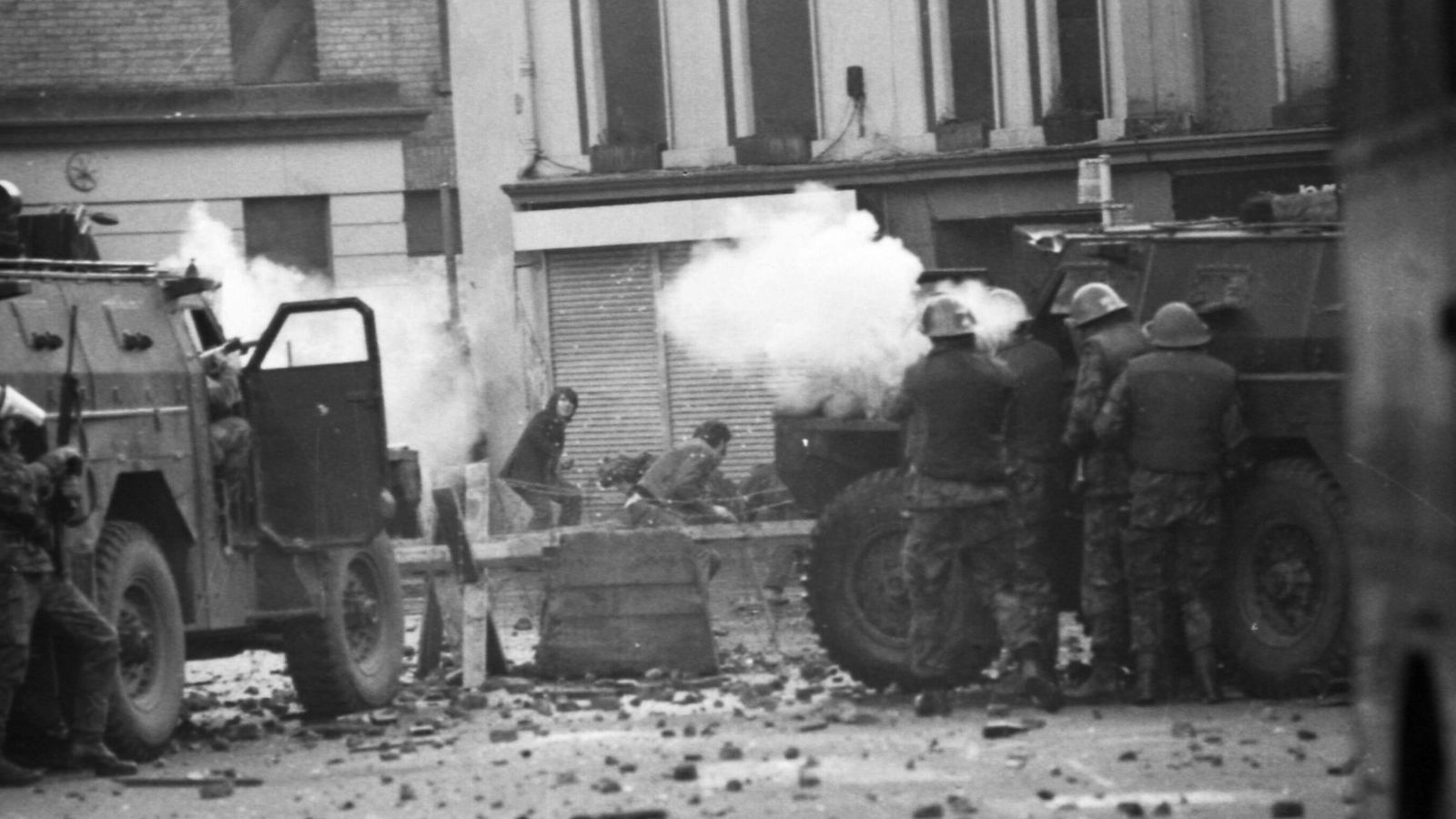
Thirteen people were shot dead when members of the Parachute Regiment opened fire following a civil rights march in Londonderry on 30 January 1972.
Only one suspect – identified as “Soldier F” – was ever charged. He was facing prosecution for double murder, but the case collapsed before it had begun.
COVID-19 rules eased in Wales and Northern Ireland for outdoor events and hospitality
COVID-19: Which coronavirus restrictions are changing in the UK and the Republic of Ireland?
COVID: Northern Ireland eases restrictions on nightclubs and hospitality
Colum Eastwood, the local MP and leader of the Social Democratic and Labour Party (SDLP), said: “The idea that unarmed people, marching for their own civil rights, for justice and democracy, were gunned down on their own streets by a special forces regiment is beyond belief.
“It’s beyond belief that it was allowed to happen, that it was lied about, that it was covered up for decades after decades.”
The victims were exonerated by a lengthy and costly public inquiry and David Cameron, the then prime minister, apologised following its publication in 2010.
The current government’s plan to halt historical prosecutions has caused deep hurt here, where the lack of justice still haunts this community.
Freya McClements, Northern Ireland editor of the Irish Times and a native of Derry, said: “Imagine if this happened in London or Liverpool or Manchester or Birmingham.
“This is why Bloody Sunday has had this long tale that has impacted not just on the families and on the city, but on the troubles and how that developed.
“Bloody Sunday was absolutely the cataclysmic turning point that sent Northern Ireland tumbling into decades of violence.”
To mark the 50th anniversary of Bloody Sunday, the city will fall silent at the precise moment the first British Army shot rang out.
Television footage of a priest waving a blood-stained handkerchief as he sought help for a wounded teenager became the defining image of the day.
That teenager was Jackie Duddy – and although five decades have passed, his sister Kay thinks about him “every day” of her life.
“That awful day, we didn’t lose a brother. We lost a generation,” she said.
Thirteen people were shot dead and a 14th fatally wounded after the British Army opened fire on crowds demonstrating in Derry/Londonderry, Northern Ireland, on Sunday 30 January 1972, against anti-Catholic discrimination.
It came at the start of the Troubles – years of conflict between Unionists, who are largely Protestant and want to remain part of the UK, and Nationalists, who are largely Catholic and want to be part of a united Ireland.
Stones were thrown, and paratroopers eventually tried to arrest as many as possible. Army documents show 21 soldiers fired a total of 108 live rounds.
The government announced an inquiry into Bloody Sunday the day afterwards. It largely cleared the Army of any blame and was branded a farce by victims’ families and their supporters.
In 1998, Tony Blair commissioned a new inquiry – it became the longest and most expensive public inquiry in British history, lasting until 2010 and costing around £200m.
It found Bloody Sunday protesters completely innocent and although there was “some firing by Republican paramilitaries”, the Army was considered responsible for the violence.
The police then spent years on new murder inquiries, but prosecutors concluded that only one solider, identified only as “Soldier F” could be charged.
Last year, two charges of murder and two of attempted murder were dropped, and the prosecution halted when evidence was deemed inadmissible.