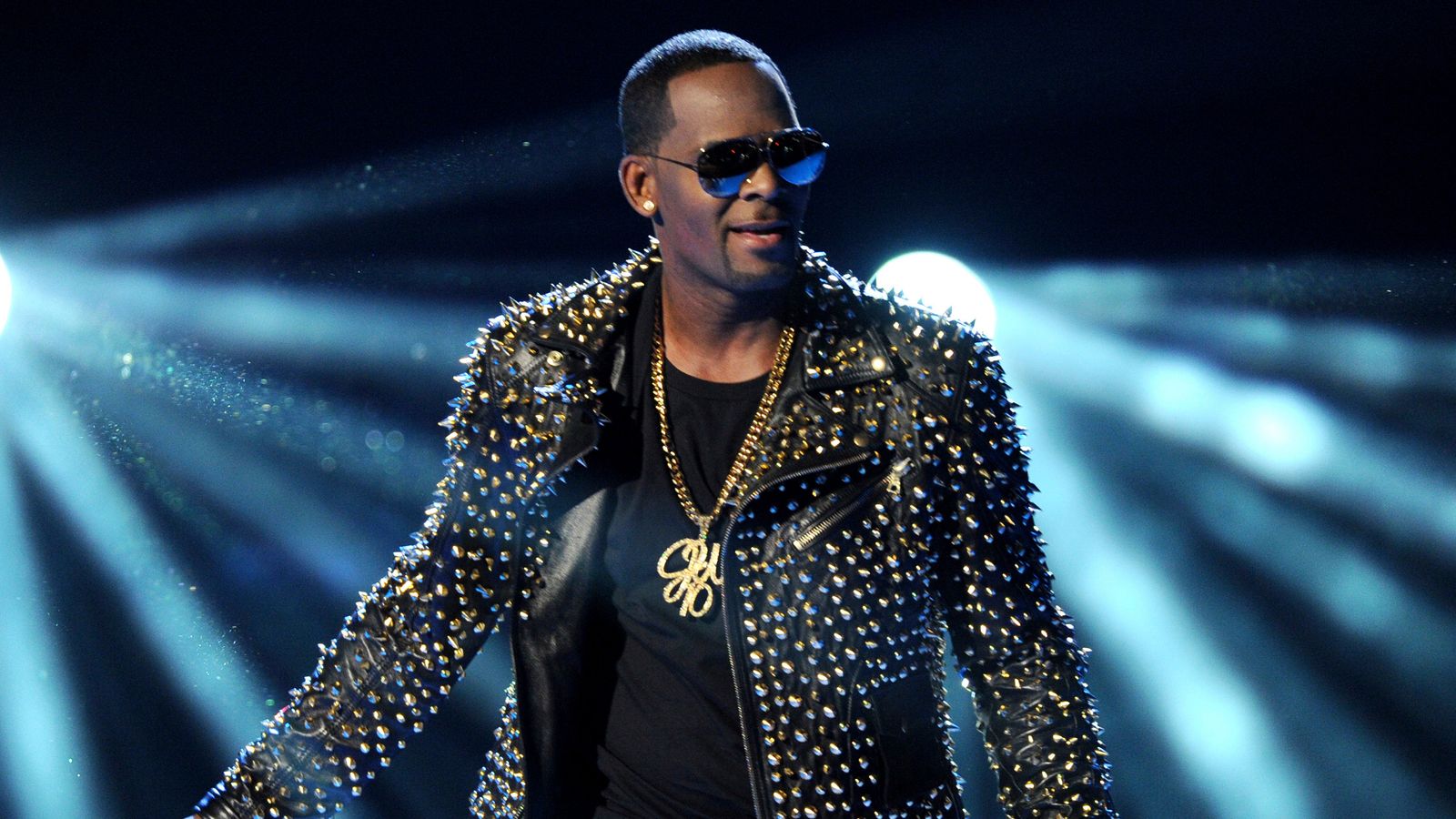
R Kelly’s trial was the culmination of decades of accusations, pointing to a predator hiding in plain sight.
Rumours and allegations about the now disgraced R&B singer date back to almost the beginning of his career – and yet, he rose to become a chart-topper, a Grammy winner, an artist who filled arenas and collaborated with huge stars; at his height, one of the biggest recording acts in the world.
The criminal details of his marriage to Aaliyah in 1994, when she was 15 and he was 27 – now detailed in open court, a former tour manager admitting he bribed an official to get a fake ID in order for the ceremony to go ahead – had always been a well-known secret. And in 2002, Kelly was charged with 21 counts of making indecent images of children. After years of delays to his trial, the singer was acquitted, but the allegations never went away.
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
Claims made over the years were silenced and brushed over, by an industry that wanted to keep the money rolling in, and fans who did not want to believe Kelly could have committed the crimes he was accused of. The world wanted to hear his music, so his unknown accusers were easy to ignore.
In the end, it was a documentary series, Surviving R Kelly, released in 2019, that became the catalyst for the singer’s trial in New York, and ultimately led to him being found guilty of all nine charges brought against him – one charge of racketeering and eight counts of violating a law which prohibits transporting people across state lines for prostitution.
For Jim DeRogatis, a journalist and music critic who wrote his first investigative report on Kelly for the Chicago Sun-Times in December 2000, with details of an allegation made against the singer dating back to 1991, it has been a long time coming.
R Kelly: Some of the key allegations from the trial
R Kelly: Jurors begin deliberations in R&B star’s sexual misconduct trial in New York
R Kelly’s lawyer compares him to Martin Luther King in closing arguments of sex abuse trial
“I always felt like I was late to the story when my partner at the Sun-Times, Abdon Pallasch, and I did the first investigative report,” he tells Sky News. “It had been going on already for nine years. We never thought when that paper came out… that this would still be ongoing in 2021.”
Just over a year later, DeRogatis was anonymously sent a videotape. “There was a manila envelope with a VHS cassette,” he says. “No markings on either.” The contents of the tape, he says, were horrifying. “Twenty-six minutes and 39 seconds showed Kelly very clearly having sexual contact with a 14-year-old girl, urinating in her mouth at one point.”
The tape led to the 2002 charges and the delayed trial in 2008. But Kelly was acquitted and continued to prey on young girls.
“He thought he was untouchable,” says DeRogatis. “There was a hubris, an ego there… He was silencing victims with money.” The most shocking thing about the case, he says, is the timeframe, and how Kelly was allowed to get away with what he was doing because of his fame.
“During that time, he’s selling 100 million albums – of his own, and [records and songs] he produced for everyone from Whitney Houston and Celine Dion to Lady Gaga and Justin Bieber. This was a cash machine for the music industry that was well aware of his behaviour and never actually acted to stop it.”
DeRogatis never stopped his reporting, helping to tell the stories of 48 different accusers over the past 21 years. But it was Surviving R Kelly that finally got people listening, he says.
“There were police officers who valiantly tried to stop his predatory behaviour. But, you know, until Surviving R Kelly brought these women into people’s living rooms in America, and they saw woman after woman after woman; 12 different women appeared on camera, telling their stories. They cannot all be liars.”
So why did justice take so long?
Kenyette Tisha Barnes, the co-founder of the #MuteRKelly movement – launched in 2017 to make calls to boycott the singer’s music and shows, and “hold accountable those who allowed this behaviour to go on for so long” – says the answer is simple: “Because these were young black girls from inner-city Chicago.”
It has taken movements such as #MeToo and Time’s Up, as well as #MuteRKelly, to get to this point, she says.
“I was a big R Kelly fan many years ago, in the ’90s. And I remember the stories. I started to hear about Aaliyah and the other young ladies, and they were always young black girls.
“I was a black girl, I’m a black woman in this country. And I’ve watched the way the entertainment industry, our whole community, maligned these young women for years. And enough was just enough.”
DeRogatis agrees it was a “problem of race”, saying: “What the 48 women whose stories I’ve told in the last 21 years have all said to me is that nobody matters less in America than young black girls. They are simply not believed, and women in general are not believed about a sexual abuse story. But black girls in particular.”
For Kelly, who last released a studio album in 2016, the guilty verdict in New York is not the end of his legal troubles; he is facing further sex abuse charges brought in Illinois and Minnesota – to which he has also pleaded not guilty.
So if the trials go ahead, there could be more allegations against the singer to come. And thanks to this first trial in New York, the spotlight is now also firmly on those who at best turned a blind eye; at worst, enabled him.
Charging the singer with racketeering meant prosecutors set out to show him as the leader of “an enterprise” where “managers, bodyguards, drivers, personal assistants and runners” were all complicit in recruiting women and girls for sex with him.
DeRogatis says there are others who should be facing charges and Barnes agrees that while Kelly was “at the top of the pyramid”, there is still “a lot of blame to go around”.
“Number one, it’s R Kelly,” she says. “Number two, it’s the people who enabled it. It’s the producers, the promoters, the runners, the people in his camp who were more interested in being aligned with a superstar than actually protecting black girls.
“And then we go further: it’s the black community. We’re all complicit. If you’ve ever played an R Kelly song, you’re complicit. If you’ve ever watched that videotape, you’re complicit. I think we have to unpack that reality that we all allowed this man to just move in the most predatory ways.”
“The racketeering statute is generally used against mob bosses and drug kingpins,” says DeRogatis. “We only have one person indicted. How are you a criminal enterprise if no one else in your alleged enterprise is being held to account?”