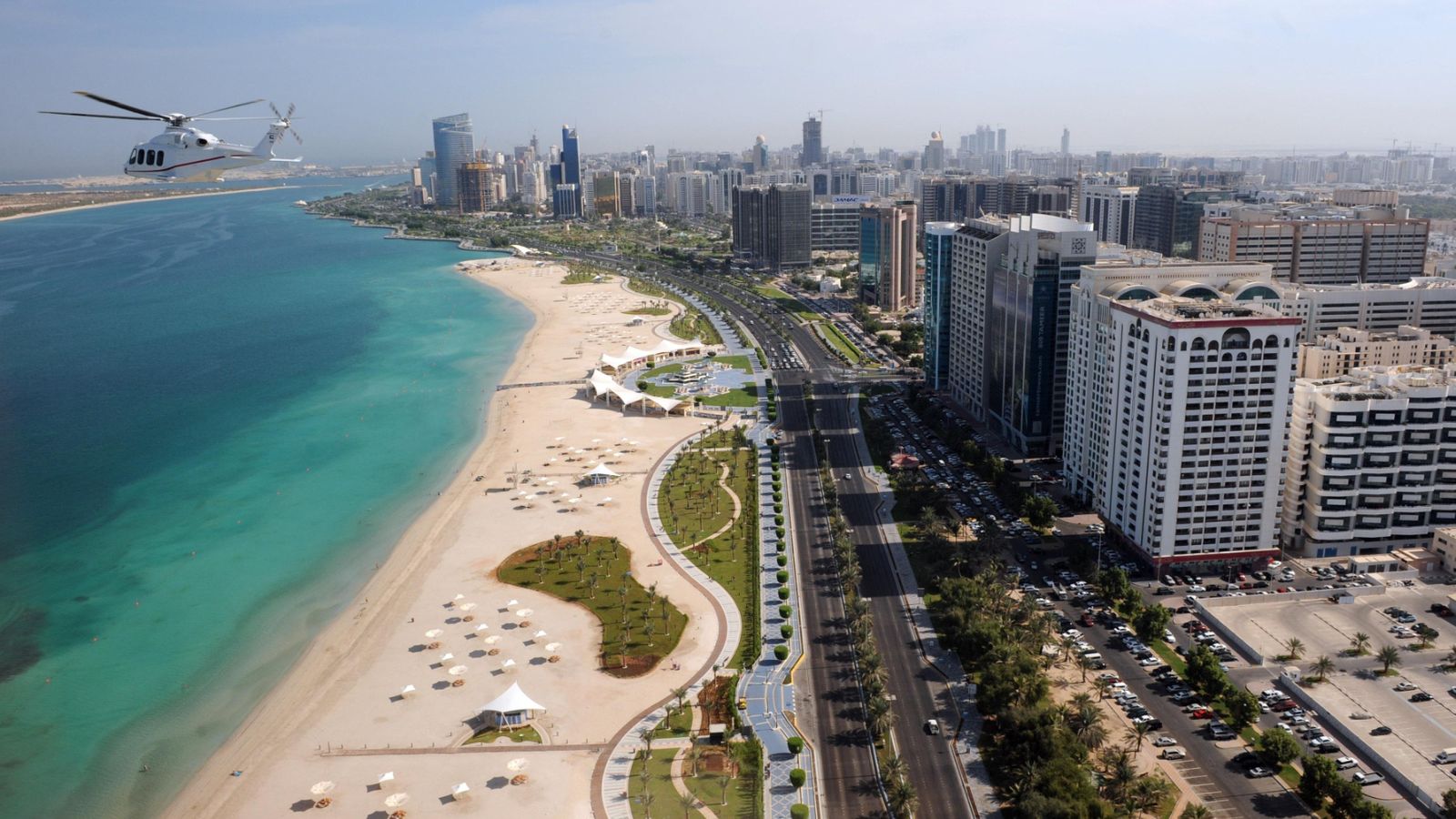
The United Arab Emirates is using drone technology to enhance its rainfall amid temperatures of over 40C.
Abu Dhabi and Al Ain are among the cities that have been drenched after the National Centre for Meteorology (NCM) implemented cloud seeding technology.
The drones fly into clouds and release electric charges, which helps water droplets merge together and form precipitation.
The country typically sees less than 100mm of rainfall a year, compared with the UK’s average of 1300 mm.
The NCM has carried out 126 cloud seeding flights since the beginning of 2021, according to Gulf Today.
This includes 14 flights since last Tuesday, with a two to three hour flight operated in most of the country’s regions.
The organisation has partly attributed increased rain to its cloud seeding efforts.
Other techniques used to stimulate rainfall in the country involve dropping salt or other chemicals into clouds, designed to accelerate the growth of water droplets.
Some studies suggest cloud seeding could increase rainfall by up to 35%, but others dispute its effectiveness.
أمطار القوع #أبوظبي #المركز_الوطني_للأرصاد #أمطار_الخير #أصدقاء_المركز_الوطني_للأرصاد #حالة_الطقس #حالة_جوية #هواة_الطقس pic.twitter.com/pL2rK2KP6a
China and India are among other countries trialling this technology.
Professor Giles Harrison, of the University of Reading, is working on the research and said it is “intended to bring blue-sky thinking to cloud and rain”.
He said: “Our project is about changing the balance of charges on the tiniest cloud droplets, a neglected aspect of clouds which could revolutionise our ability to manipulate rainfall in areas that need it most.”
صور الرادار ثلاثية الأبعاد لحركة تكون السحب#أمطار #أمطار_الخير #استمطار #تلقيح_السحب #المركز_الوطني_للأرصاد
3D Radar images of cloud formation over the area#rain #cloudseeding #national_Center_of_Meteorology pic.twitter.com/TuPBK9kU3g
“Water scarcity is one of the biggest problems facing humanity, and climate change is providing more uncertainty around rainfall,” said Dr Keri Nicoll, another academic who conducted preliminary tests in Bath.
She said initiatives to improve rainfall are crucial in parts of the world that are “really struggling for water”.