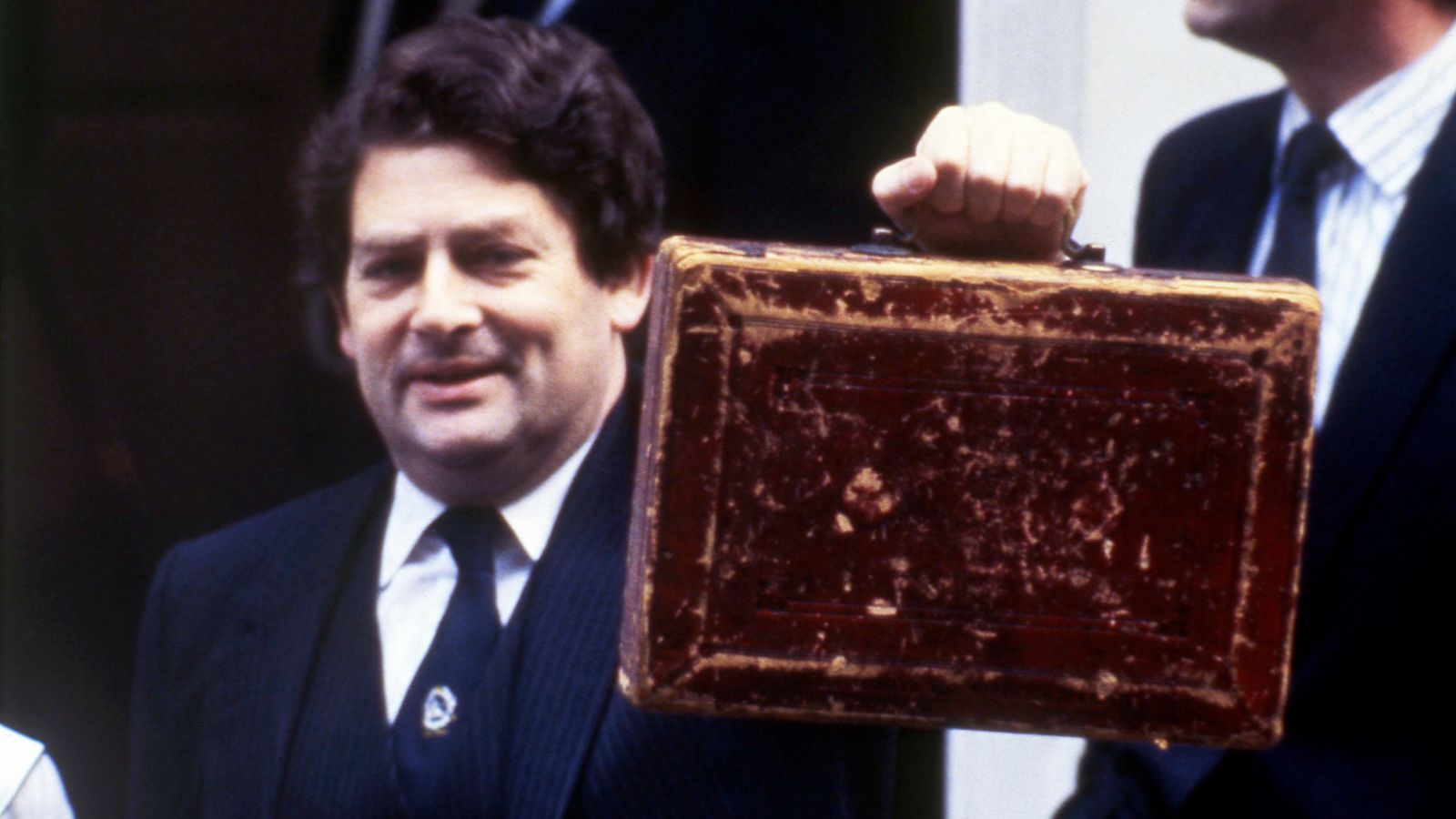
Nigel Lawson, chancellor to Margaret Thatcher, has died at the age of 91.
He leaves behind five of his six children, including TV chef Nigella Lawson and journalist Dominic Lawson. One of his daughters, Thomasina, died aged 32.
Born in Hampstead, northwest London, on 11 March 1932, the son of the owner of a tea-trading firm, he climbed his way to the top of British politics after an education at Westminster School and Oxford University.
His political life started at Oxford, where he studied Philosophy, Politics and Economics – like many other politicians – but he began his working life carrying out national service as a Royal Navy officer.
Lord Lawson, as he was to become, then became a financial journalist, writing for the Financial Times and The Sunday Telegraph, before becoming editor of The Spectator.
After 14 years as a journalist, in 1970 he stood to become an MP, unsuccessfully, for the Eton and Slough seat before eventually winning the now-defunct Leicestershire constituency of Blaby four years later.
When the Conservatives won the election in 1979 under Mrs Thatcher, she made him financial secretary to the Treasury and her policies at the time clearly reflected his influence.
Sir Bernard Ingham: Margaret Thatcher’s longest-serving press secretary dies aged 90
A love troika: For Reagan and Thatcher, Gorbachev was the man the West could do business with
Liz Truss recreates Margaret Thatcher’s outfit ‘down to last detail’ at Tory leadership debate, Twitter users say
She then promoted him to energy secretary, where he helped prepare for what he called “inevitable” full-scale strikes in the coal industry, which had been nationalised by Labour prime minister Clement Attlee.
But it was as chancellor that Mr Lawson ensured he would go down in the history books.
Tax cuts, the Big Bang and the Lawson Boom
The second longest-serving chancellor after Gordon Brown, Mr Lawson was key to Mrs Thatcher’s economic policies – and success.
After getting the job in 1983 he pushed ahead with tax reforms, reducing corporation taxes and lowering National Insurance contributions for the lower-paid, while extending the VAT base.
From 1986, his public image grew after he reduced the standard rate of personal income tax and unemployment began to fall.
He also managed to turn around government finances from a budget deficit of £10.5bn in 1983 to a surplus of £3.9bn in 1988 and £4.1bn in 1989.
However, the government’s current account deficit increased from below 1% GDP to almost 5% in three years.
Mr Lawson managed to honour his promise to bring taxation rates down, with the basic rate going from 30% to 25%, and the top tax rate from 60% to 40%. He also removed other higher rates so nobody paid above 40% in personal tax.
One of his major triumphs was the Big Bang of 1986, which saw the City’s financial markets deregulated and London strengthened as a financial capital – but in 2010, he admitted the “unintended consequence” of that was the 2007 financial crisis.
He even had a period of economic growth named after him. The Lawson Boom saw the UK economy on the up after 1986, with unemployment halved.
However, that led to a rise in inflation to 8% in 1988 and interest rates doubled to 15% within 18 months, with critics accusing Mr Lawson of unleashing an inflationary spiral due to his policies.
In his 1992 memoir, written just after he stepped down as an MP, Mr Lawson admitted the 1987 manifesto was not properly thought through and if it had not been for the economic growth, the manifesto would have been a disaster.
“As it was, it was merely an embarrassment,” he said.
Clashes with Thatcher
While he was Mrs Thatcher’s right-hand man, the pair did not always see eye-to-eye and he was overruled in cabinet when he opposed introducing a poll tax to replace local government financing.
There was also the now-infamous 1988 budget, which took nearly two hours for Mr Lawson to announce as there were continuous interruptions and protests from opposition parties.
The then deputy leader of the Scottish National Party, Alex Salmond, was suspended from the Commons for his constant interruptions.
Mrs Thatcher and her chancellor also clashed over the exchange-rate mechanism (ERM) membership in 1985, with Mr Lawson – ironically, as he became a Brexiteer – believing membership was the only way forward to help convince the markets the UK was committed to fiscal discipline.
It proved to be one of Mrs Thatcher’s most tumultuous meetings with her senior ministers as she single-handedly faced them down after Mr Lawson had spoken separately to all of the ministers present to persuade them to ambush her.
Mr Lawson later said he had considered resigning after she said their arguments did not convince her, but he was dissuaded by colleagues. Mrs Thatcher was persuaded to sign up to the ERM five years later by Mr Lawson’s successor, John Major.
The prime minister’s relationship with her chancellor took another dive when she re-employed economist Alan Walters in 1989 as her personal economic adviser, with Mr Lawson at loggerheads with them over the ERM.
He threatened to resign if Mrs Thatcher did not sack Mr Walters over his lack of support for the ERM. Mrs Thatcher wrote in a private memo that was “absurd” and urged him to rethink – and Mr Lawson quit.
National Archive files released in 2017 revealed the extent Mr Walters was briefing against Mr Lawson, including telling Mrs Thatcher that Mr Lawson’s position over the ERM was having a devastating impact on the UK economy.
Mr Lawson’s resignation was seen as the beginning of the end for Mrs Thatcher, with her foreign secretary Geoffrey Howe resigning shortly after – and Mrs Thatcher resigned in 1990 after Michael Heseltine decided to challenge her for leadership of the Conservative Party.
Post-Thatcher
Mr Lawson remained as a backbencher until 1992, when he was elevated to the House of Lords with a life peerage, and was known as Lord Lawson of Blaby.
Months after he stood down as an MP, he lost five stone after his doctor told him his knee problems would not stop if he continued to carry the weight.
It dramatically changed his appearance and he published The Nigel Lawson Diet Book, which became a best seller.
Previously 17 stone and 5ft 9, he had been an easy target for political cartoonists – although it did not bother him – and he admitted after losing weight: “I was certainly a fat man.
“It came up gradually, and by the time I was chancellor, certainly, that was the thing the cartoonists seized on; that was part of the image – no doubt about it.”
Mr Lawson used his time away from the Commons to occasionally appear as a guest on daughter Nigella’s cookery shows.
He also served on the advisory board of the Conservative magazine Standpoint.
Two wives, six children
Mr Lawson was married twice. His first wife was former ballet dancer Vanessa Salmon with whom he had Dominic (the journalist), Thomasina (who died of breast cancer aged 32), Nigella (the TV chef) and Horatia. After they divorced, Ms Salmon died of liver cancer aged 48.
His second wife was former Commons researcher Therese Maclear, who he married the same year he divorced Ms Salmon. They had son Tom and daughter Emily before they divorced in 2008.
In 2011, he found love again at the age of 79 with 42-year-old Dr Tina Jennings, a former banker who was previously married to New Zealand’s richest man.
However, they split up two years later, with Dr Jennings reportedly finding it hard to go regularly to France, which Mr Lawson did every weekend.
Controversial support for Brexit
In 2009, Mr Lawson was caught up in the parliamentary expenses scandal after he was accused of claiming £16,000 in overnight allowances by registering his farmhouse in Gascony, southwest France, as his main residence.
In 2013, the former chancellor pushed for the UK to leave the EU and ahead of the 2016 referendum he was appointed chairman of the Vote Leave campaign.
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
At the time, he was living in France and in 2018 started to apply for his official French residency card.
His critics accused him of hypocrisy for living in France yet campaigning for the UK to leave the EU, but he said he did not believe the issue of Britons living in other EU countries was a big problem in the Brexit negotiations.
In 2019, Mr Lawson returned to live in the UK after putting his Gascony mansion on the market. He said it was to be close to his children and grandchildren.
Climate scepticism
In opposition to Mrs Thatcher, who helped put climate change on the agenda, Mr Lawson was very sceptical of the concept and denied global warming is taking place to such a large degree as many scientists say.
He wrote a letter in 2004 criticising the Kyoto Protocol and claiming there were substantial scientific uncertainties.
As a member of the House of Lords Economics Affairs Select Committee, he carried out an inquiry into climate change in 2005 and recommended the Treasury take a more active role in climate policy.
The report said there was a mismatch between the economic costs and the benefits of climate policy – which kicked off a tussle between him and Michael Grubb, chief economist of the Carbon Trust.
He contributed to the 2007 documentary The Great Global Warming Swindle and in 2008 published a book called An Appeal to Reason: A Cool Look at Global Warming.
In the book, he admitted global warming is happening and will have negative consequences but said the impact of those changes will be moderate rather than apocalyptic, and criticised “alarmist” politicians and scientists.
He was heavily denounced by climate scientists and the UK’s chief scientific adviser at the time, Sir John Beddington, who privately told Mr Lawson he had “incorrect” and “misleading” claims in the book.
But that did not stop him airing his views, and in 2009 he launched a new thinktank called The Global Warming Policy Foundation.
His journalist son, Dominic Lawson, is also a climate change sceptic.